Question Each student will complete a concept map PowerPoint presentation based on the “interview” of the partner they use for the Functional Health Patterns Assignment. During the assessment, the student will identify a pertinent medical diagnosis and then will utilize the concept map template to build a PowerPoint for the process of identifying a 3-part nursing diagnosis. Concept Map of the Clinical Care Plan for a 38-Year-Old Male Patient Diagnosed with Cardiac Arrhythmias (NANDA diagnosis is related to, as evidenced by). Students must use a NANDA-approved nursing diagnosis, as found in Chapter 17 of the course text. Students will present their concept map to the class or small group setting using a power point. Presentation will be graded by peers.
Concept Map of the Clinical Care Plan for a 38-Year-Old Male Patient Diagnosed with Cardiac Arrhythmias
Concept Map of the Clinical Care Plan for a 38-Year-Old Male Patient Diagnosed with Cardiac Arrhythmias

Hello and welcome to my presentation. This presentation creates a concept map of the clinical care plan for a 38-year-old male patient diagnosed with cardiac arrhythmias. The presentation covers patient information, the medical diagnosis, the risk factors for the medical diagnosis, and the nursing diagnosis. It also presents patient goals, diagnostic tests, and assessments to support the diagnosis, as well as the interventions proposed, the rationale for interventions, patient education, and learning goals.

The patient is a 38-year-old male who presented himself to the clinic with complaints of irregular heartbeats, lightheadedness, and feeling dizzy. He also reported having pain, discomfort, and flutters in the chest. He is married with two kids. The patient is physically overweight and has a BMI of 29.7.

The most probable medical diagnosis is cardiac arrhythmia. This medical diagnosis is arrived at based on the symptoms the patient presents, such as irregular heartbeats, and a review of the patient’s health and lifestyle history. It is also based on objective diagnostic tests.

The major risk factors for cardiac arrhythmia include advanced age, chronic conditions including diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure and coronary artery disease. Cardiac arrhythmia can also develop due to being overweight and obese, as well as poor lifestyle and dietary choices such as fast foods, alcohol and substance use, and physical inactivity (Chung et al., 2020). It can also develop due to cardiomyopathy, stress, and anxiety.

The nursing diagnosis based on the presented symptoms, physical assessment, and review of health history is decreased cardiac output related to alteration in heart rate, rhythm, and conduction as evidenced by irregular heart rate and irregular heartbeat rhythm. The goals for the patient include Goal 1, aimed at achieving and maintaining regular HR, rhythm, and blood pressure within normal ranges to help the patient have adequate cardiac output and reduce the frequency and occurrence of arrhythmias; Goal 2, to achieve 180 minutes of physical activity per week in order to help manage his current weight problem and improve heart efficiency, and Goal 3 to improve his understanding of the prescribed medications which is essential for improving the adherence to medication plan and reduce risk of medication errors.
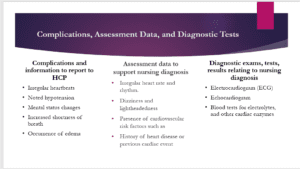
The possible complications and information to report include any issues of hemodynamic instabilities, including hypotension and changes in the patient’s mental status, irregular heartbeats, noted shortness of breath, and the occurrence of edema. The reported information includes the time the complications were observed, the frequency, progression, and severity. Assessment data that supports the nursing diagnosis include the presence of irregular heart rate and rhythm, the patient feeling dizzy and lightheaded, and underlying risk factors such as the patient being overweight and his dietary choices. The diagnostic exams and tests for the diagnosis include an ECG to specifically test cardiac arrhythmias and severity, an echocardiogram to test the heart’s internal structure and functioning, and blood tests specifically electrolytes and cardiac enzymes, to determine the presence of metabolic imbalances and possible cardiac injury.
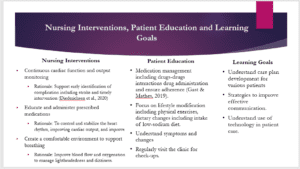
The nursing interventions for the patient include continuous cardiac function and output monitoring. Continuous monitoring supports the identification of complications such as stroke early as they occur and the implementation of timely intervention (Diederichsen et al., 2020). The second intervention is to educate and administer the presc
